Why Choosing the Right Spindle Makes or Breaks Your CNC Router Performance
A spindle for cnc router machine operations is the beating heart of precision manufacturing. It’s the rotating component that holds your cutting tools and delivers the torque, speed, and accuracy needed for everything from aerospace aluminum to composite materials.
Quick Answer: Top CNC Router Spindle Recommendations
• 1.5 kW Water-Cooled (ER11) – Best for wood, plastics, light aluminum
• 2.2 kW Water-Cooled (ER20) – Ideal for aluminum, steel, continuous duty
• ATC Spindles (ISO30) – Maximum productivity for production environments
• Air-Cooled Options – Simple installation, lower maintenance
The difference between a standard router motor and an industrial spindle is like comparing a hand drill to a precision machining center. Modern CNC spindles use four angular contact bearings for runout under 0.01mm, integrated VFD control for precise RPM management, and water cooling systems that maintain thermal stability during extended cuts.
Whether you’re cutting aircraft components or heavy industrial parts, your spindle choice affects everything from surface finish quality to tool life. A 2.2 kW spindle running at 24,000 RPM can handle materials that would destroy a trim router in minutes.
This guide covers the technical details that matter most: power ratings, cooling methods, collet systems, and VFD integration. We’ll help you match spindle specifications to your material requirements and production goals.
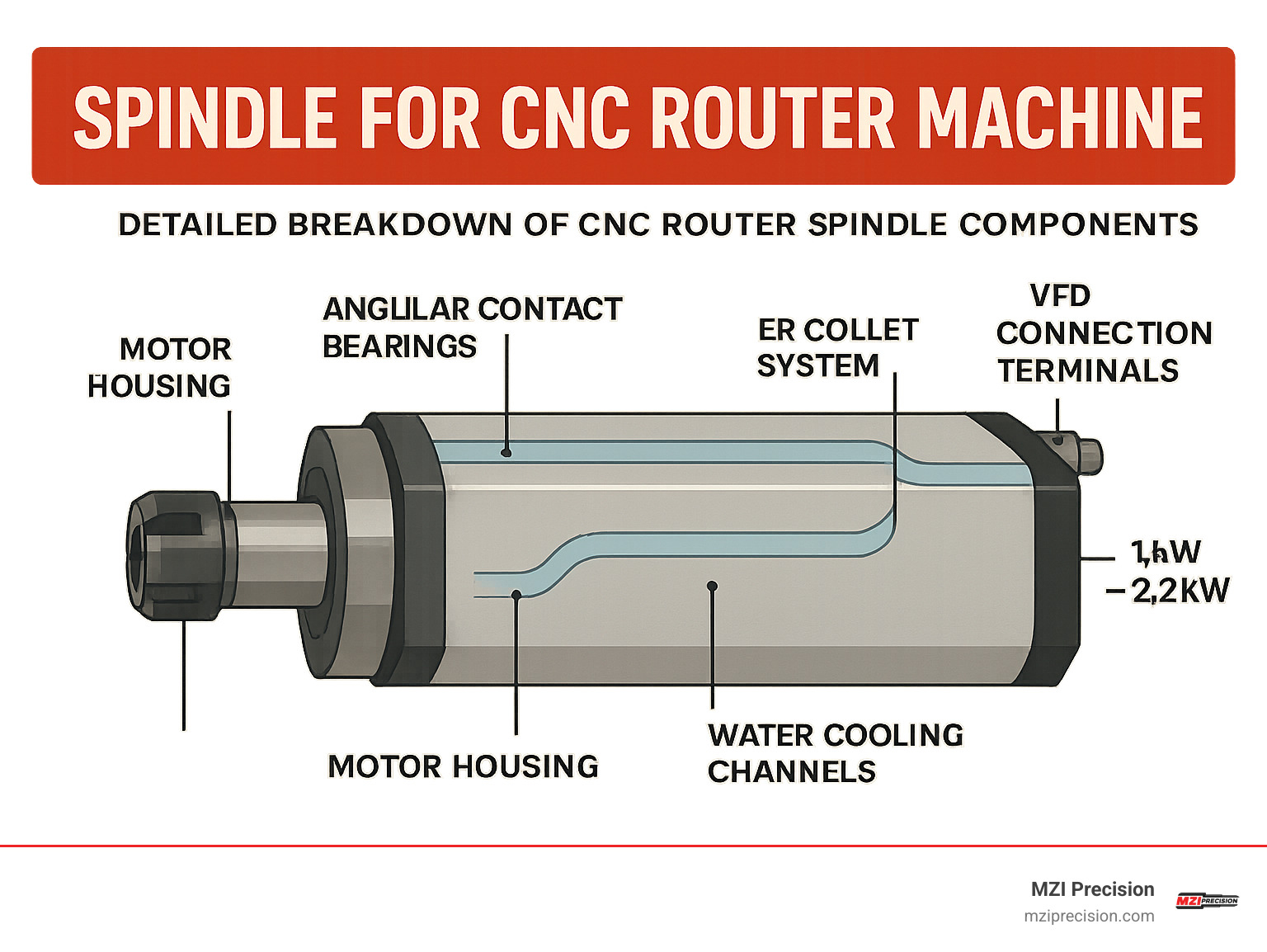
Simple spindle for cnc router machine glossary:
– CNC Machine Spindle
– grinding spindle
– cnc multi spindle machine
What Makes a CNC Router Spindle Tick?
A spindle for cnc router machine is essentially a purpose-built, ultra-precise electric motor. At its core, a rotor spins inside a stator, turning electromagnetic energy into rotation. Four matched angular-contact bearings (usually two 7005 and two 7002 in a 2.2 kW unit) keep runout below 0.01 mm, so your tool path stays exactly where the G-code says it should.
Precision doesn’t stop at the bearings. The ER collet system grips the tool with a self-locking taper; tighten the nut with the correct 22 mm/30 mm wrenches and the shank is locked in place for heavy cuts. Torque curves matter more than peak horsepower, so quality spindles are engineered to deliver nearly flat torque over the working range instead of one narrow power peak.
Industrial spindles also differ from trim-router motors in three big ways:
- Integrated motor design – the rotor is the tool shaft, eliminating couplings and their vibration.
- VFD speed control – 0-10 V or digital commands give single-RPM precision from the CAD/CAM file straight to the spindle.
- Thermal management – water or high-flow air cooling keeps the housing at a consistent temperature, preventing thermal growth that would shift tolerances.
Inside the housing you’ll also find a hardened, dynamically balanced shaft with a drawbar running down its center (manual or pneumatic for ATC units) and coolant channels that whisk heat away from the windings. Miss on any one of these details and you lose surface finish, tool life, or both.
The difference shows up in data too. Peer-reviewed studies on high-speed spindle precision confirm that bearing preload, vibration control and thermal stability directly correlate with part accuracy and spindle life.
Selecting the Ideal Spindle for CNC Router Machine Operations
Choosing the right spindle for cnc router machine work boils down to a handful of numbers:
• Power (kW): 1.5 kW is plenty for plastics and light aluminum; 2.2 kW handles aggressive cuts in aluminum or mild steel.
• RPM range: Most water-cooled units peak at 24 000 RPM. Stay below 15 000 RPM for steel; push closer to the top end for aluminum and composites.
• Voltage: A 2.2 kW spindle on 220 V draws ~10 A; the same spindle on 110 V needs ~20 A. That single fact usually settles the voltage debate.
• Collet size: ER11 (max 7 mm shank) keeps weight down for fine work. ER20 (max 13 mm shank) accepts 1/2-inch cutters for higher MRR.
• Duty cycle: Look for 100 % if you run production shifts.
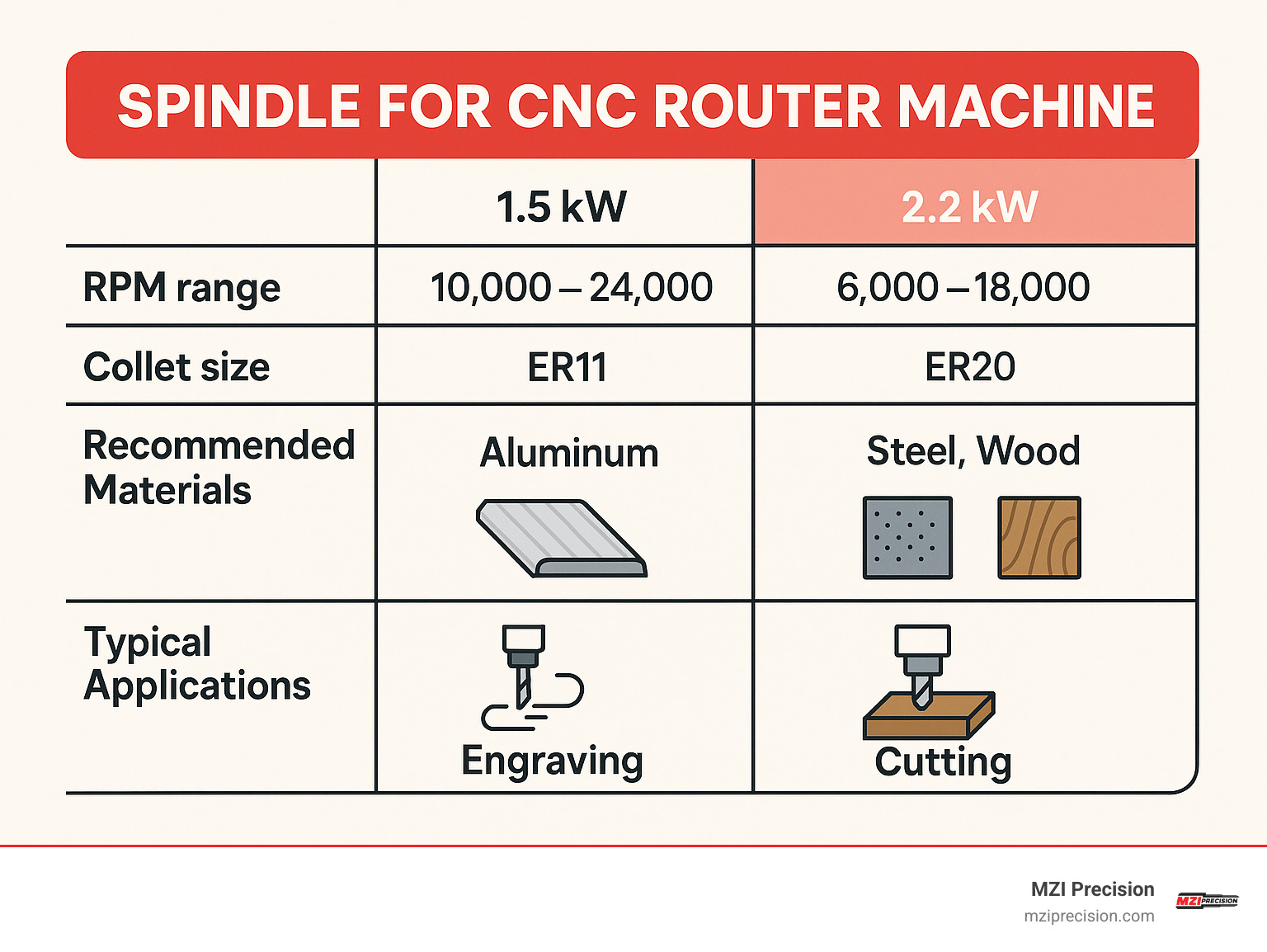
Matching Power & Speed to Material Removal Rates
• Steel: Use a 4-pole, 800 Hz motor; keep RPM between 8 000 and 15 000 where torque is highest.
• Aluminum: Loves 18 000-24 000 RPM. Even a 1.5 kW spindle rips through 6061 if chip evacuation is good.
• Composites: Variable speed is king. Dial in just enough RPM to cut cleanly without delamination.
Chip load = feed ÷ (RPM × flutes). Because RPM is under VFD control, your chip load stays predictable, extending tool life.
Why Collet Size Matters
ER11 is perfect for micro-machining; ER20 offers the clamping force required for large end mills. Replace worn collets—runout often tracks back to a $20 consumable, not the $1 000 spindle.
Automatic Tool Change (ATC) vs Manual
ATC spindles (ISO30 taper) can slash cycle times by up to 90 %. The retrofit is possible but expensive—budget 40-60 % of a new machine when you include the changer, pneumatics, and control integration.
Cooling Wars: Water-Cooled vs Air-Cooled Spindles
Water cooling wins on noise and thermal stability. A small pump circulates coolant through channels in the housing, holding temperatures within ±5 °C even on multi-hour jobs. Bearings live longer, and you avoid the chip-blast that air-cooled fans create.
Air-cooled units, however, skip hoses, pumps, and leak risk. For light intermittent work—prototype aluminum plates, occasional composite panels—they’re perfectly adequate and easier to install.
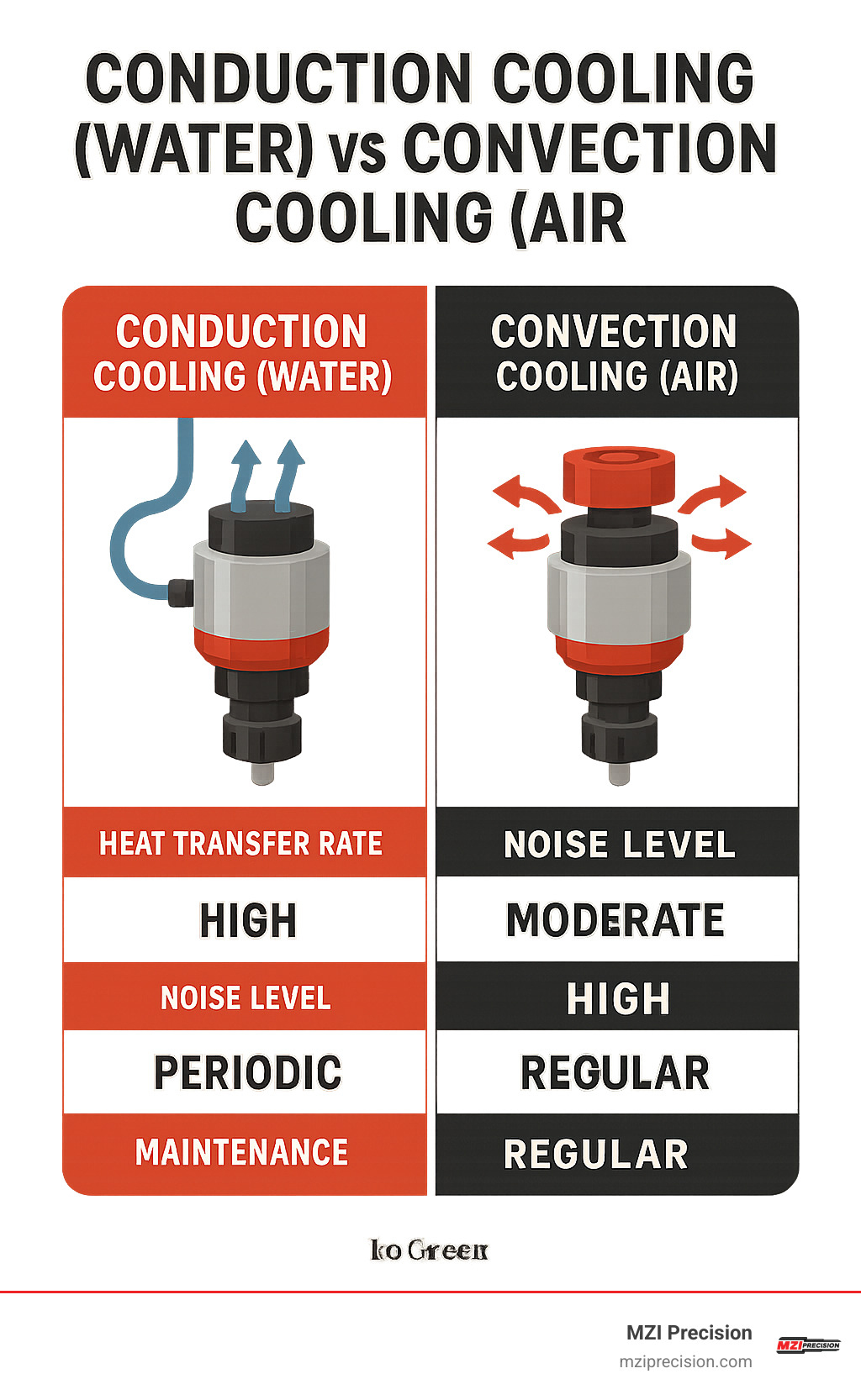
Advantages & Trade-Offs for Industrial Floors
• Continuous duty: Water-cooled. No thermal pauses.
• Maintenance: Pumps and coolant changes (water) vs. fan cleaning (air).
• Shop environment: Choose water if you need whisper-quiet operation or tight tolerances in a hot building. Pick air if simplicity matters more than long-haul thermal control.
Installation, VFD Programming & Safety Essentials
Electrical first: a 2.2 kW spindle on 220 V needs a 15-20 A breaker. The VFD converts that single-phase supply into the three-phase U-V-W output that the spindle expects.
Programming is simple once you know the menu flow: MODE → set P-parameters → ENTER. Typical settings are 400 Hz max frequency (≈24 000 RPM), 3-5 s acceleration and deceleration, and motor-overheat protection.
Shielded cable from VFD to spindle, plus an EMI inlet filter, keeps electrical noise out of motion-control signals.
Safety items you can’t skip:
• E-stop wired to cut VFD and coolant simultaneously
• Proper earth grounding on the spindle housing
• PPE—glasses and hearing protection whenever chips are flying
Step-by-Step Wiring
U→Pin 3, V→Pin 1, W→Pin 2, Pin 4 unused. Ground the green wire to the machine frame. If your spindle has a temperature sensor, land it on the VFD’s thermistor inputs so the drive can shut down on over-temp.
Coolant pumps can be switched by the VFD’s auxiliary relay: coolant on whenever RPM > 0, off when the spindle stops.
Controlling Speed & Direction From CNC Software
G-code handles everything: M3 clockwise, M4 counter-clockwise, M5 stop. The S-word sets RPM, and a 0-10 V analog line (or Modbus, if available) feeds that command to the VFD for closed-loop speed control.
Maintenance, Runout Testing & Troubleshooting
Think of maintenance as cheap insurance. Inspect collets monthly, clean the taper, and check bearing noise while the spindle is idling. Catch issues early and a rebuild is a scheduled service, not a line-stopping emergency.
Measuring & Minimizing Spindle Runout
Use a dial indicator against a precision test bar. Below 0.005 mm (0.0002 in) is the goal. High readings? Verify collet, then tool holder. Only after those checks point to the bearings is a rebuild required.
Common Faults and Quick Fixes
• Overload trips: Reduce depth of cut or feed; check tool sharpness.
• Cooling alarm: Inspect pump and coolant flow; clear any obstructions.
• Collet slip: Two-wrench tightening and fresh collets usually solve it.
When in doubt, call MZI Precision—our technicians can walk you through vibration analysis, preload checks, or a full spindle rebuild without guesswork.
Frequently Asked Questions About Industrial CNC Router Spindles
These are the questions we hear most often from machine shops looking to upgrade or replace their spindle for cnc router machine systems. Let’s explore the practical details that matter for your operations.
What power supply do I need for a 2.2 kW spindle?
Getting the electrical requirements right from the start saves headaches later. A 2.2 kW spindle needs 220V power with a 15-20A circuit breaker for safe, efficient operation. The VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) converts your shop’s single-phase power into the three-phase output that the spindle motor requires.
Here’s why 220V makes sense: running a 2.2 kW spindle on 110V would draw about 20 amps, which exceeds most standard 15A household circuits. You’d need heavy-gauge wiring and larger breakers, making the installation more complex and expensive.
Most industrial shops already have 220V available, making this the practical choice. The VFD handles the conversion seamlessly, and you get better efficiency with lower current draw. Plus, your electrical connections run cooler, which means safer operation and longer component life.
How does spindle speed affect tool life in stainless steel?
Stainless steel is notorious for eating cutting tools if you approach it wrong. The key is understanding that stainless steel work-hardens when it gets hot, turning your expensive carbide tools into expensive paperweights.
Optimal spindle speeds for stainless typically range from 8,000-15,000 RPM, depending on your tool diameter and cutting conditions. This is much slower than the 18,000-24,000 RPM you might use for aluminum. The slower speeds generate less heat, preventing that work-hardening effect that destroys tools.
Feed rates become equally important. Higher feed rates with lower speeds keep the cutting edge moving through fresh material before heat can build up. Think of it like this: you want to cut the material before it realizes what’s happening to it.
Flood coolant isn’t optional with stainless – it’s mandatory. The coolant carries away heat and lubricates the cutting action. Without proper coolant flow, even perfect speeds and feeds won’t save your tools from premature wear.
Can I retrofit an ATC spindle onto an older CNC router?
This question comes up a lot, especially when shops want to boost productivity on existing machines. The short answer is yes, but it’s not a simple bolt-on upgrade.
ATC retrofit requires several major modifications to your existing machine. You need compatible spindle mounting (the new spindle diameter might differ from your current setup), a tool changer mechanism, pneumatic or hydraulic systems for the drawbar operation, and complete control system integration.
The machine’s structural rigidity becomes critical. ATC spindles generate different forces during tool changes, and your machine frame must handle these loads without flexing. Older machines sometimes need reinforcement to maintain accuracy.
Retrofit costs often run 40-60% of a new machine’s price when you factor in all the required modifications. This makes the cost-benefit analysis crucial. If you’re running high-mix, low-volume work with frequent tool changes, the productivity gains might justify the investment. For simpler operations, manual tool changes might make more economic sense.
The control system integration can be the trickiest part. Your existing CNC controller needs to communicate with the tool changer, manage the drawbar operation, and coordinate the entire tool change sequence. Sometimes this requires controller upgrades or replacement.
Conclusion
The world of spindle for cnc router machine technology keeps evolving, and it’s exciting to see where we’re headed. Ceramic bearings are revolutionizing spindle life expectancy, offering superior temperature resistance and precision retention compared to traditional steel bearings. While they cost more upfront, these advanced bearings maintain accuracy longer and handle the heat generated by high-speed operations much better.
IoT monitoring represents the next frontier in spindle management. Modern systems track everything from vibration patterns to temperature fluctuations and power consumption. This smart approach to predictive maintenance programs dramatically reduces unplanned downtime by catching problems before they become expensive failures. Instead of waiting for a spindle to break down during a critical production run, you get early warnings that let you schedule maintenance at convenient times.
The newest generation of smart spindles comes equipped with integrated sensors that provide real-time feedback on cutting forces, operating temperature, and vibration levels. This constant stream of data enables adaptive machining strategies that automatically optimize tool life and surface finish quality based on actual cutting conditions.
High-speed spindles operating at 25,000-90,000 RPM are becoming more accessible for specialized industrial manufacturing applications. These speeds open up new possibilities for micro-machining and ultra-precision work that wasn’t economically feasible just a few years ago.
Whether you’re machining aerospace components or heavy industrial parts, your spindle choice ripples through every aspect of your operation. The precision delivered by four angular contact bearings, the thermal stability of water cooling systems, and the reliability of proper VFD integration all contribute to your bottom line success.
At MZI Precision, we’ve seen how spindle performance directly impacts manufacturing profitability. Our expertise in industrial manufacturing spindle repair and rebuilding helps keep production lines running smoothly when equipment needs professional attention. We understand that every hour of downtime costs money, which is why we’re committed to getting your spindles back to peak performance quickly.
The investment you make in a quality spindle for cnc router machine pays dividends in precision, productivity, and long-term profitability. Choose your spindle specifications carefully, maintain it properly with regular inspections and lubrication, and it will deliver years of reliable service that keeps your shop competitive.
For comprehensive information about our industrial spindle services, contact our team. We proudly serve aerospace, defense, and industrial manufacturing customers across California and throughout the United States, bringing decades of spindle expertise to every project.



