Why Spindles Are Crucial in Manufacturing
When it comes to precision in industrial manufacturing, the spindle is an essential component. If you’re wondering why spindles are so important in manufacturing, here’s a quick summary:
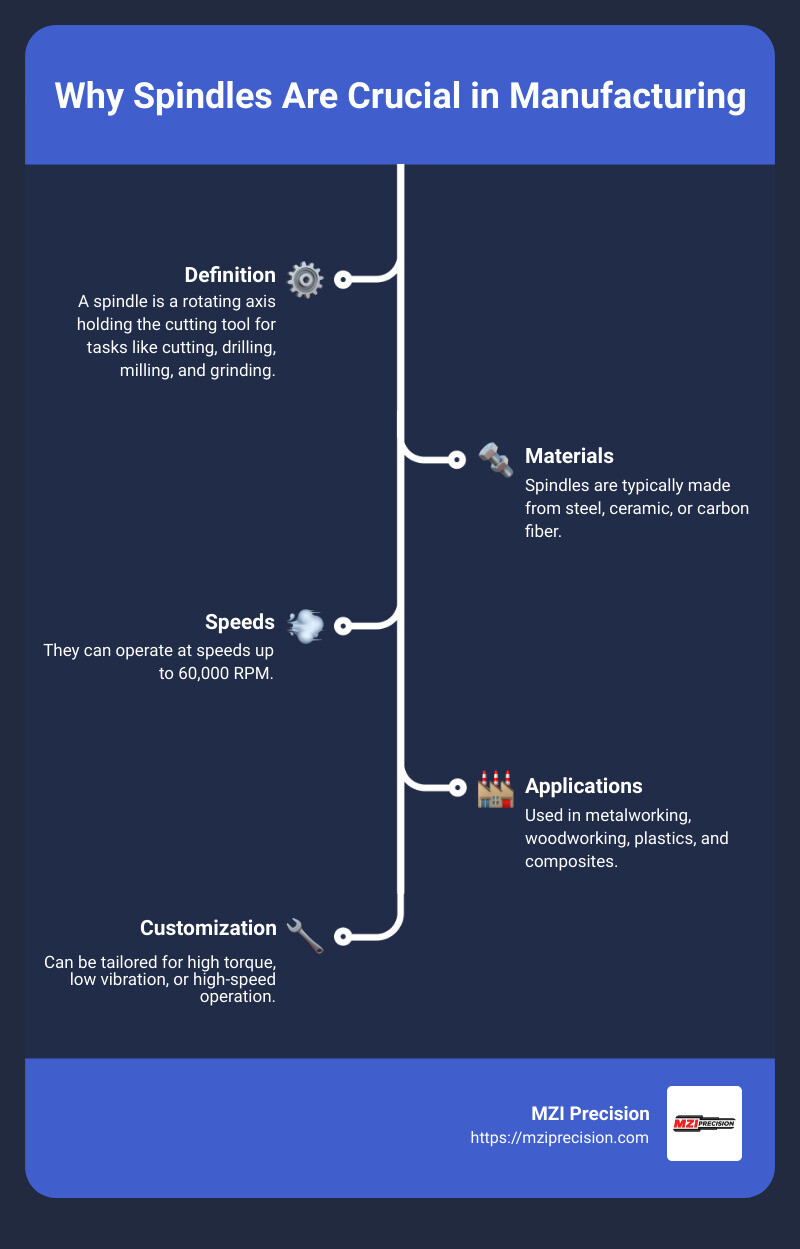
- Definition: A spindle is a rotating axis that holds the cutting tool, enabling tasks like cutting, drilling, milling, and grinding.
- Materials: Typically made of steel, ceramic, or carbon fiber.
- Speeds: Can operate at very high speeds, up to 60,000 RPM.
- Applications: Used in metalworking, woodworking, plastics, and composites.
- Customization: Can be tailored for high torque, low vibration, or high-speed operation.
In manufacturing, precision and durability are paramount. Spindles are vital for ensuring accurate, repeatable, and high-quality results across a variety of industries, including aerospace, medical, and consumer goods.
What is a Spindle?
A spindle is a critical component in both biology and industrial manufacturing, serving different but equally important functions.
Spindle Definition
In simple terms, a spindle is a rotating axis of a machine which holds the cutting tool or the workpiece. It provides the necessary speed and power to perform tasks like cutting, drilling, milling, and grinding.
In biology, the spindle is an assembly of microtubules that forms during cell division to separate chromosomes. It ensures that each daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes.
Spindle Apparatus
The spindle apparatus in a cell is a structure made of microtubules that forms during cell division. It helps in the segregation of chromosomes into the daughter cells. This apparatus is crucial for ensuring genetic material is evenly divided.
In manufacturing, the spindle apparatus includes various parts like the rotating shaft, bearings, and motor. This assembly is responsible for the high precision and efficiency required in industrial processes.
Spindle Shape
In biology, the spindle shape is often described as spindle-shaped or fusiform, meaning it is wider in the middle and tapers at both ends. This shape is essential for its function during cell division.
In manufacturing, spindles can vary in shape depending on their function. They can be cylindrical, tapered, or even customized to meet specific needs. The shape directly impacts the spindle’s performance, including its speed, torque, and stability.
Understanding what a spindle is and its various forms helps in appreciating its role in both biological processes and industrial applications. Whether separating chromosomes or cutting metal, spindles are indispensable tools for precision and efficiency.
Next, let’s dive into the different types of industrial manufacturing spindles and their unique applications.
Types of Industrial Manufacturing Spindles
When it comes to industrial manufacturing, spindles are the unsung heroes. They do the heavy lifting, enabling precision and efficiency in various processes. Let’s explore the main types of industrial manufacturing spindles: machine tool spindles, suspended spindles, and grasped spindles.
Machine Tool Spindles
Machine tool spindles are the most common type found in manufacturing. These spindles are integral to machines like CNC machines, lathes, and milling machines. They hold and rotate cutting tools, allowing for precise shaping and drilling of materials.
Key Features:
- High Speed: Machine tool spindles can achieve speeds up to 60,000 RPM.
- Versatility: They are used in metalworking, woodworking, plastics, and composites.
- Customization: These spindles can be tailored for high torque, low vibration, or high-speed operations.
Example: In CNC machining, these spindles hold the cutting tool, enabling detailed and accurate shaping of metals and plastics.
Suspended Spindles
Suspended spindles are designed to hang vertically, often used in applications where space is limited. These spindles are typically found in drilling and grinding machines.
Key Features:
- Space-Saving: Ideal for vertical operations where floor space is at a premium.
- Precision: Offer high precision in drilling and grinding tasks.
- Flexibility: Can be used in various orientations, making them versatile for different applications.
Example: In grinding machines, suspended spindles rotate grinding wheels to smooth and finish surfaces, ensuring high-quality outputs.
Grasped Spindles
Grasped spindles are held in place by a mechanism, usually in horizontal applications. These spindles are commonly found in milling and turning machines.
Key Features:
- Stability: Provides a stable platform for horizontal operations.
- High Torque: Suitable for heavy-duty tasks requiring significant torque.
- Durability: Built to withstand rigorous use in industrial settings.
Example: In milling machines, grasped spindles rotate cutting tools to remove material and shape workpieces to exact specifications.
Summary Table
| Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Tool Spindles | High speed, versatile, customizable | CNC machines, lathes, milling |
| Suspended Spindles | Space-saving, precise, flexible | Drilling, grinding |
| Grasped Spindles | Stable, high torque, durable | Milling, turning |
Understanding these types of industrial manufacturing spindles helps in selecting the right one for your specific needs. Each type has unique strengths, making them suitable for different applications and ensuring optimal performance.
Next up, let’s discuss the crucial aspects of spindle repair and rebuilding to keep your operations running smoothly.
The Function of Spindles in Manufacturing
Spindles are the heart of many manufacturing machines. They hold and rotate tools or workpieces, enabling cutting, drilling, milling, and grinding. But let’s break down their function further.
Spindle Function
Spindles provide the necessary power and speed for various machining tasks. They are essential for precision and efficiency in manufacturing. Whether you’re working with metal, wood, or plastic, the spindle ensures that your tools operate smoothly and accurately.
Spindle Fibers
In the context of manufacturing, spindle fibers refer to the rotational elements that transmit power from the motor to the spindle shaft. These fibers, or components, ensure that the spindle can maintain high speed and torque, which are crucial for cutting and shaping materials.
Spindle Apparatus
The spindle apparatus in manufacturing is a complex assembly of parts, including the motor, bearings, and the spindle shaft. This apparatus must be finely tuned to reduce vibration, minimize heat, and ensure precision. In high-speed operations, like those in the aerospace or medical industries, the performance of the spindle apparatus can make or break the quality of the final product.
Spindle in Cell Division
Interestingly, the term “spindle” is also used in biology. During cell division, a structure called the spindle apparatus forms to separate chromosomes. This biological process is crucial for life, just as the mechanical spindle is vital for manufacturing.
Hyman, a researcher from the University of Cambridge, highlighted the importance of understanding spindle formation during his studies in the 1980s. Similarly, understanding the mechanical spindle’s function helps manufacturers achieve high precision and quality.
Next up, let’s discuss the crucial aspects of spindle repair and rebuilding to keep your operations running smoothly.
Anatomy of a Spindle
Understanding the anatomy of a spindle is crucial for anyone involved in industrial manufacturing. Let’s break down the main components: the shaft, whorl, and cop, as well as the materials used in spindle construction.
Shaft
The shaft is the central part of the spindle, acting as the backbone. It can be made from various materials such as wood, metal, bone, or plastic. The shaft’s thickness affects how fast the spindle spins; narrower shafts cause the spindle to spin faster.
In industrial settings, shafts are often made of steel, ceramic, or carbon fiber to withstand high speeds and heavy loads. The shaft is where the spinner inserts twist, either by turning it between fingers or rolling it on another part of their anatomy.
Many spindles feature a point at the top of the shaft for fixing the thread. This can be a simple length of shaft to tie the thread around, a shaped notch, or even a hook.
Whorl
The whorl is a weight added to many types of spindles to provide momentum. It can be made from materials like wood, metal, glass, plastic, stone, clay, or bone. The shape and mass distribution of the whorl affect how the spindle spins. For example:
- Center-weighted whorls spin very fast but for a shorter duration.
- Rim-weighted disk-shaped whorls spin longer but slower.
Whorls can be located near the top, middle, or bottom of the spindle shaft. The location affects the spindle’s stability, with bottom whorl spindles generally being more stable.
Cop
The cop is the collection of newly spun yarn wound around the spindle. Although not initially part of the spindle, it becomes integral as it forms. The shape and weight of the cop can impact the spindle’s momentum and spinning efficiency. Cops can be wound in various shapes like balls, cones, or footballs.
Spindle Parts and Materials
Spindle parts include the shaft, whorl, and any additional components like hooks or notches. These parts can be made from a wide range of materials, each chosen for specific properties:
- Steel: Durable and strong, ideal for high-speed operations.
- Ceramic: Lightweight and heat-resistant, perfect for precision tasks.
- Carbon Fiber: Extremely strong and lightweight, used in advanced applications.
Quick Facts and Tips
- Material Choice: Selecting the right material for your spindle is crucial. For example, steel is great for durability, while ceramic offers precision.
- Whorl Location: The location of the whorl can significantly affect your spindle’s performance. Bottom whorl spindles are generally more stable.
Understanding these components and their functions can help you maintain and optimize your spindles for better performance and longer lifespan.
Next up, let’s discuss the crucial aspects of spindle repair and rebuilding to keep your operations running smoothly.
History and Evolution of Spindles
Historical Spindles
The spindle has a rich history dating back thousands of years. Early spindles were simple tools made from readily available materials like wood, bone, and stone. These early versions were essential for creating thread and yarn, which were crucial for making textiles.
Spindle Whorls
A key component of historical spindles is the whorl. This weight, often disk-shaped, was added to the spindle to provide momentum, making it easier to spin fibers into yarn. Whorls were made from various materials including clay, stone, and later, metal. They were often decorated, reflecting the culture and artistic sensibilities of their time.
Spindle in Neolithic Times
In Neolithic times, the spindle was a tool. Around 10,000 BCE, as humans transitioned from nomadic lifestyles to settled agricultural communities, the need for textiles grew. The spindle allowed for the efficient production of thread, which could then be woven into cloth. This simple yet effective tool played a vital role in the development of early civilizations.
Spindle in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution brought significant advancements to spindle technology. The introduction of machine tools in the 18th century transformed manufacturing. Spindles became more complex and were integrated into machinery like spinning wheels and looms. These innovations drastically increased the speed and efficiency of textile production.
For example, the spinning jenny, invented by James Hargreaves in 1764, used multiple spindles to spin several threads simultaneously. This was a game-changer, exponentially increasing productivity and laying the groundwork for modern manufacturing.
Next, we’ll dive into the crucial aspects of spindle repair and rebuilding to keep your operations running smoothly.
Spindle Repair and Rebuilding
When it comes to keeping your manufacturing operations running smoothly, spindle repair and rebuilding are essential. Spindles are the backbone of many machines, and any malfunction can lead to significant downtime and loss of productivity.
Why Spindle Repair is Crucial
Spindles can wear out or break due to high-speed operations, heavy loads, or continuous use. Over time, components like bearings, seals, and the shaft itself can degrade. This can lead to poor performance, increased vibration, and even complete failure.
MZI Precision specializes in diagnosing and repairing these issues. Our team performs an in-depth analysis to identify the root cause of the problem. This includes:
- Vibration analysis: To detect imbalances.
- Thermal imaging: To identify overheating components.
- Run-out testing: To measure spindle accuracy.
The Rebuilding Process
Rebuilding a spindle involves more than just replacing broken parts. It’s about restoring the spindle to its original or even better condition. At MZI Precision, we follow a meticulous process:
- Disassembly: We carefully take apart the spindle to inspect each component.
- Cleaning: Components are cleaned using solvents and polishing techniques.
- Inspection: Each part is measured and checked for wear and damage.
- Repair or Replacement: Faulty parts are either repaired or replaced with high-quality components.
- Reassembly: The spindle is reassembled in a clean room environment to avoid contamination.
- Testing: We validate the spindle’s performance through speed, temperature, and vibration tests.
OEMs Rebuilt Spindles
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) often provide rebuilt spindles as a cost-effective alternative to buying new ones. These spindles are refurbished to meet OEM specifications and come with warranties. MZI Precision also offers OEM-quality rebuilt spindles, ensuring you get reliable performance without the high cost.
Spindle Maintenance
Regular maintenance can extend the life of your spindles and prevent unexpected failures. Here are some tips:
- Lubrication: Regularly lubricate bearings and other moving parts.
- Alignment checks: Ensure the spindle is properly aligned to avoid unnecessary wear.
- Temperature monitoring: Keep an eye on operating temperatures to catch overheating early.
- Vibration monitoring: Regularly check for unusual vibrations that could indicate a problem.
By following these maintenance practices, you can keep your spindles running smoothly and extend their lifespan.
Next, let’s answer some frequently asked questions about spindles to clear up any remaining doubts.
Frequently Asked Questions about Spindles
What is the function of spindle fibers?
Spindle fibers are crucial in cell division, specifically during mitosis and meiosis. These fibers form part of the spindle apparatus, which is responsible for separating sister chromatids into two daughter cells. Think of them as the ropes that pull the chromosomes apart, ensuring each new cell gets the correct set of chromosomes.
What is a spindle in biology?
In biology, a spindle refers to the spindle apparatus that forms during cell division. This structure is made up of proteins and microtubules and is essential for distributing chromosomes evenly between two daughter cells. The term “mitosis” itself comes from the Greek word “mitos,” meaning warp thread, highlighting the spindle’s thread-like appearance.
What is spindle shape?
Spindle shape can vary depending on its application. In biological terms, spindle fibers form a football-like shape during cell division. In industrial manufacturing, spindles have cylindrical or tapered shapes to hold and rotate cutting tools or grinding wheels. The design ensures precision and stability during high-speed operations.
By understanding these fundamental aspects of spindles, from their biological roles to their industrial applications, we can appreciate their critical importance in both nature and technology.
Next, we’ll dive into the conclusion to summarize the key points and discuss the significance of spindle maintenance and MZI Precision’s expertise.
Conclusion
In summary, spindles are indispensable components in industrial manufacturing. They hold and rotate cutting tools and grinding wheels, ensuring precision and stability in high-speed operations. Whether in metalworking, woodworking, or composite material processing, spindles play a critical role in achieving the accuracy and repeatability required for modern manufacturing.
The Importance of Spindle Maintenance
Maintaining spindles is crucial for several reasons:
- Performance: Regular maintenance ensures that spindles operate at peak efficiency, providing the high-speed and high-precision performance that modern manufacturing demands.
- Longevity: Proper care and timely repairs can significantly extend the life of a spindle, sometimes up to 15 years.
- Cost-Efficiency: Preventive maintenance can help avoid costly downtime and expensive repairs, ultimately saving money in the long run.
MZI Precision Expertise
At MZI Precision, we understand the critical role that spindles play in your operations. Our expertise lies in:
- Design and Build: We use cutting-edge technology and world-class NSK bearings to deliver high-speed, high-precision spindles.
- Repair and Rebuilding: Our comprehensive repair and rebuilding services ensure that your spindles are always in top shape, minimizing downtime and maximizing performance.
- Maintenance: We offer regular maintenance services to prevent common causes of spindle failure, such as wear and tear, contaminants, and improper lubrication.
We are committed to providing exceptional service and support, ensuring your spindles deliver unparalleled performance and accuracy. For more information or to discuss your spindle needs, contact us.
By focusing on maintenance and leveraging our expertise, you can ensure your spindles remain reliable and efficient, driving success in your manufacturing operations.



